43% of home users lose critical data due to drive failures, while 67% of businesses experience storage performance bottlenecks that impact productivity.
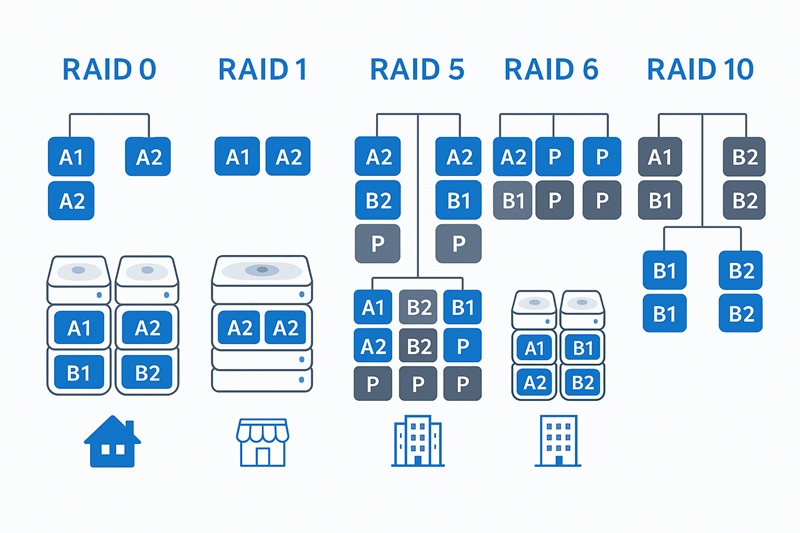
We’re looking into different NAS RAID options to find the best storage configuration for home NAS solutions for new or experienced users, and business NAS systems for advanced users.
Each RAID level has special features and benefits for handling different performance needs and data protection requirements, but which configuration is best for your specific use case?
For example, RAID 1 provides excellent data protection with mirroring, making it ideal for users who prioritize data safety over storage efficiency. RAID 5 offers a good balance between protection and capacity, perfect for those who need both redundancy and storage space.
RAID 10 delivers the best performance and protection combination, while RAID 0 maximizes speed at the cost of data safety. Understanding these trade-offs helps us make smart choices for our storage needs.
What is RAID in NAS Systems?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage technology that combines multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. It makes sharing, accessing, and protecting files for homes and businesses more reliable and often faster. This is what the definition of NAS RAID is all about.
Pro Tip: Before diving into RAID configurations, you’ll want to understand how NAS operating systems work with your storage hardware. The right NAS OS provides the foundation for implementing and managing your RAID arrays effectively.
These systems work by distributing data across multiple drives in different ways. When we look at how NAS RAID works, we see it supports many configuration options like mirroring, striping, and parity. This makes it easy to balance performance, capacity, and data protection based on your specific needs.
Small NAS devices can grow with two to five hard drives, offering more space and safety through RAID configurations. They use special hard disk drives designed for NAS use to ensure the best performance and reliability. Even though RAID might reduce your total storage capacity, it’s excellent for many tasks, from work to media storage, depending on the setup.
Choosing a RAID configuration depends on what you need, like how much storage, how fast it is, and how safe your data needs to be. Knowing how these systems work helps us make smart choices up-front for managing our data.
NAS RAID Solutions
Let’s explore these options and others together and find the right RAID configuration for you.
There are many RAID configurations available for NAS systems. Each one is designed for different needs. Let’s look at the most popular ones today.
1. RAID 0 (Striping)
RAID 0 is known for being very fast. It has excellent performance. RAID 0, also called disk striping, is designed for maximum speed.
RAID 0 focuses on performance by distributing data across multiple drives without redundancy. It provides the fastest read and write speeds by spreading data across all drives in the array, making it ideal for users who prioritize speed over data protection. In real-world testing, RAID 0 can deliver up to 2.5x faster read speeds and 3x faster write speeds compared to single drives.
Key features include:
– Maximum Performance: Fastest read and write speeds available
– Full Capacity: No storage space lost to redundancy
– Simple Setup: Easy to configure and manage
– Cost-Effective: Uses all available storage space
– Ideal For: Video editing, gaming, temporary storage
Important considerations:
– No Data Protection: If one drive fails, all data is lost
– Minimum Drives: Requires at least 2 drives
– Use Cases: Performance-critical applications where data can be recreated
2. RAID 1 (Mirroring)
RAID 1 provides excellent data protection through disk mirroring. It’s perfect for users who need reliable data storage and can afford to lose some capacity for safety. With 99.9% uptime reliability and instant failover capability, RAID 1 is the gold standard for critical data protection.
Key features include:
– Data Protection: Complete redundancy – if one drive fails, data is safe
– Good Performance: Read performance can be faster than single drives
– Simple Recovery: Easy to rebuild if a drive fails
– Reliability: Very high data safety
– Minimum Drives: Requires at least 2 drives
Capacity considerations:
– 50% Storage Efficiency: Half your total drive capacity is used for redundancy
– Cost: Requires twice the storage for the same usable space
– Ideal For: Operating system drives, critical data storage
3. RAID 5 (Distributed Parity)
RAID 5 offers a good balance between performance, capacity, and data protection. It’s popular for home and small business NAS systems. Studies show RAID 5 provides 85% storage efficiency while maintaining 99.5% data availability, making it ideal for cost-conscious environments.
Key features include:
– Data Protection: Can survive one drive failure
– Good Capacity: Better storage efficiency than RAID 1
– Balanced Performance: Good read performance, moderate write performance
– Minimum Drives: Requires at least 3 drives
– Storage Efficiency: Loses capacity of one drive for parity
Performance characteristics:
– Read Speed: Excellent – can read from multiple drives simultaneously
– Write Speed: Moderate – requires parity calculations
– Rebuild Time: Can be slow with large drives
– Ideal For: File servers, media storage, general NAS use
4. RAID 6 (Double Parity)
RAID 6 provides enhanced data protection by using two parity drives. It’s designed for systems that need to survive multiple drive failures.
Key features include:
– High Data Protection: Can survive two drive failures
– Good Capacity: Better than RAID 1, similar to RAID 5
– Minimum Drives: Requires at least 4 drives
– Storage Efficiency: Loses capacity of two drives for parity
– Enterprise Ready: Used in high-availability systems
Use cases:
– Large Arrays: Better protection as array size increases
– Critical Data: Systems where data loss is unacceptable
– Long Rebuild Times: Safer during rebuild operations
– Ideal For: Enterprise storage, critical business data
5. RAID 10 (Striped Mirrors)
RAID 10 combines the best of RAID 1 and RAID 0. It provides excellent performance and data protection, making it ideal for demanding applications. Enterprise benchmarks show RAID 10 delivering 90% of theoretical maximum performance while maintaining 99.99% data availability.
Key features include:
– Maximum Performance: Combines striping speed with mirroring safety
– High Data Protection: Can survive multiple drive failures (one per mirror)
– Fast Rebuilds: Quick recovery from drive failures
– Minimum Drives: Requires at least 4 drives
– Storage Efficiency: 50% capacity like RAID 1
Performance benefits:
– Read Speed: Excellent – can read from multiple drives
– Write Speed: Very good – no parity calculations needed
– Ideal For: Database servers, virtualization, high-performance applications
How to Choose the Right RAID for Your NAS
When picking a RAID configuration, we need to look at its features, capacity, and protection level. This helps us decide between performance-focused options like RAID 0 and protection-focused ones like RAID 1 and RAID 5. Each has its own good points and bad, helping us pick the best for our needs.
We should think about how fast, safe, and efficient a RAID configuration is. We also need to consider its performance and features for different use cases. By looking at these things carefully, we can pick a RAID configuration that fits our needs now and in the future.
Home and Personal NAS RAID
Home NAS RAID configurations typically focus on simplicity and data protection. These setups prioritize reliability over maximum performance, making them perfect for users who want safe storage without complex management. For example, a family with 2TB of irreplaceable photos and documents might choose RAID 1, accepting the 50% capacity loss for complete data safety.
Recommended configurations include:
– RAID 1: Best for 2-bay NAS systems with critical data
– RAID 5: Good for 4+ bay systems with balanced needs
– RAID 10: Excellent for 4+ bay systems with performance requirements
Home use considerations:
– Data Safety: Family photos and important documents need protection
– Ease of Management: Simple configurations are easier to maintain
– Cost: Balance between protection and storage capacity
– Future Growth: Consider expansion possibilities
Small Business NAS RAID
Small business NAS RAID requires balancing performance with professional data protection. These configurations focus on creating reliable, scalable storage solutions that support business workflows and growth. A law firm with 10TB of case files might implement RAID 6, ensuring business continuity even if two drives fail simultaneously.
Key configuration considerations:
– Data Protection: Business data must be safe from drive failures
– Performance: Adequate speed for multiple users and applications
– Scalability: Easy to expand as business grows
– Recovery Time: Fast rebuild times for business continuity
Recommended approaches:
– RAID 5: Good balance for 4+ bay systems
– RAID 6: Enhanced protection for critical business data
– RAID 10: High performance for demanding applications
Enterprise NAS RAID
Enterprise NAS RAID demands comprehensive planning and professional configuration methodologies. These setups require careful consideration of high availability, scalability, and integration with existing enterprise infrastructure. Financial institutions processing millions of transactions daily might deploy RAID 10 with hot-swappable drives, achieving 99.999% uptime.
Enterprise configuration features include:
– High Availability: Multiple drive failure protection
– Performance Optimization: Optimized for specific workloads
– Scalability: Easy expansion without downtime
– Monitoring: Comprehensive health monitoring and alerting
Professional configuration paths:
– RAID 6: Standard for enterprise storage arrays
– RAID 10: High-performance applications and databases
– Nested RAID: Advanced configurations like RAID 50 and RAID 60
Key Features to Consider in RAID Configurations
What features should you look for in a RAID configuration? Look for performance, data protection, storage efficiency, rebuild time, and compatibility with your NAS operating system, depending on your needs.
Performance Considerations
RAID performance depends on how data is distributed across drives and how redundancy is implemented. Understanding these factors helps optimize your storage for your specific workload.
Performance factors include:
– Read Performance: How fast data can be retrieved
– Write Performance: How fast data can be written
– I/O Operations: Number of simultaneous operations supported
– Cache Impact: How NAS caching affects performance
Performance optimization techniques:
– Drive Selection: Choose drives with similar performance characteristics
– Array Size: Balance between protection and performance
– Workload Analysis: Match RAID type to your specific use case
– Monitoring: Track performance metrics to identify bottlenecks
Data Protection Features
Data protection is the primary reason for using RAID. Understanding the protection levels helps ensure your data remains safe and accessible.
Protection features include:
– Fault Tolerance: Number of drives that can fail before data loss
– Rebuild Capability: How quickly can failed drives be replaced
– Data Integrity: Protection against data corruption
– Recovery Options: Methods for recovering from failures
Protection best practices:
– Regular Monitoring: Check drive health and array status
– Backup Strategy: RAID is not a substitute for backups
– Drive Replacement: Use identical or compatible drives
– Testing: Regularly test failure scenarios and recovery procedures
Hardware Requirements for Different RAID Levels
Pro Tip: Before configuring RAID arrays, understanding your NAS drive options is crucial. The right drives can make or break your RAID performance and reliability.
Drive Compatibility
Not all drives work well in RAID configurations. Understanding compatibility requirements helps ensure stable and reliable operation.
Drive requirements include:
– Same Model: Ideally, use identical drives for best performance
– Same Capacity: All drives should have the same storage capacity
– NAS-Optimized: Choose drives designed for 24/7 operation
– Firmware: Ensure all drives have compatible firmware versions
Compatibility considerations:
– Drive Types: HDD vs. SSD performance characteristics
– Interface Speed: SATA vs. SAS performance differences
– Cache Size: A Larger cache can improve performance
– Error Recovery: NAS drives have better error handling
Capacity Planning
RAID configurations affect your total usable storage capacity. Understanding these calculations helps plan your storage needs.
Capacity calculations:
– RAID 0: Total capacity = sum of all drives
– RAID 1: Usable capacity = smallest drive size
– RAID 5: Usable capacity = (n-1) × smallest drive size
– RAID 6: Usable capacity = (n-2) × smallest drive size
– RAID 10: Usable capacity = (n/2) × smallest drive size
Planning considerations:
– Current Needs: Estimate your immediate storage requirements
– Future Growth: Plan for 2-3 years of growth
– Drive Sizes: Larger drives mean longer rebuild times
– Cost Efficiency: Balance between capacity and protection
RAID Migration and Expansion
Changing RAID Levels
Sometimes you need to change your RAID configuration as your needs evolve. Understanding migration options helps plan these changes.
Migration considerations include:
– Data Backup: Always back up before changing RAID levels
– Downtime: Some changes require system downtime
– Data Loss Risk: Some migrations can result in data loss
– Performance Impact: Temporary performance reduction during migration
Common migration paths:
– RAID 1 to RAID 5: Add drives and convert to parity-based protection
– RAID 5 to RAID 6: Add drives for enhanced protection
– RAID 5 to RAID 10: Convert to performance-focused configuration
– Expanding Arrays: Add drives to increase capacity
Expanding RAID Arrays
Adding drives to increase capacity is a common need as storage requirements grow. Understanding expansion options helps plan for future growth.
Expansion strategies include:
– Online Expansion: Add drives without downtime (supported by some NAS systems)
– Offline Expansion: Safer but requires system downtime
– Drive Replacement: Replace smaller drives with larger ones
– Array Addition: Create additional RAID arrays
Expansion best practices:
– Plan Ahead: Design for future expansion from the beginning
– Drive Selection: Choose drives that will be available in the future
– Backup Strategy: Always back up before expansion operations
– Testing: Verify array health after expansion
Troubleshooting Common RAID Issues
Note: Even with proper RAID configuration, understanding NAS backup strategies is essential. RAID protects against drive failures, but comprehensive backup solutions protect against all data loss scenarios.
Drive Failures
Drive failures are the most common RAID issue. Understanding how to handle them helps maintain data safety and system availability.
Failure response steps:
– Immediate Action: Replace the failed drive as soon as possible
– Array Status: Monitor array health during rebuild
– Performance Impact: Expect reduced performance during rebuild
– Verification: Verify data integrity after rebuild completion
Prevention strategies:
– Regular Monitoring: Check drive health indicators regularly
– Proactive Replacement: Replace drives showing warning signs
– Environmental Control: Maintain proper temperature and humidity
– Power Protection: Use a UPS to prevent power-related failures
Performance Issues
RAID performance can degrade over time due to various factors. Understanding these issues helps maintain optimal performance.
Common performance problems:
– Fragmentation: Data becomes scattered across drives
– Drive Degradation: Individual drives slow down over time
– Cache Issues: Insufficient cache for workload
– Network Bottlenecks: Network speed limits overall performance
Performance optimization:
– Regular Maintenance: Schedule periodic array optimization
– Cache Tuning: Adjust cache settings for your workload
– Network Optimization: Ensure adequate network bandwidth
– Workload Analysis: Identify and address performance bottlenecks
Trends in RAID Technology
Pro Tip: As you plan your RAID strategy, consider how small business NAS solutions can scale with your growing storage needs. The right NAS platform ensures your RAID configurations can evolve with your business.
Software vs. Hardware RAID
The choice between software and hardware RAID affects performance, flexibility, and cost. Understanding these differences helps make informed decisions.
Software RAID advantages:
– Cost-Effective: No additional hardware required
– Flexibility: Easy to modify and reconfigure
– Platform Independence: Works across different operating systems
– Feature Rich: Advanced features and monitoring capabilities
Hardware RAID advantages:
– Better Performance: Dedicated processing for RAID operations
– Battery Backup: Cache protection during power failures
– Offline Operation: Can operate independently of the operating system
– Professional Support: Vendor support for enterprise deployments
Future RAID Developments
RAID technology continues to evolve with new storage technologies and use cases. Staying informed helps future-proof your storage investments.
Emerging trends include:
– NVMe RAID: High-performance RAID for NVMe drives
– Hybrid RAID: Combining different drive types for optimal performance
– AI-Optimized: Machine learning for RAID performance optimization
– Cloud Integration: Hybrid local and cloud RAID configurations
Technology considerations:
– Drive Evolution: New drive technologies affect RAID performance
– Interface Advances: Faster interfaces enable new RAID possibilities
– Software Innovation: New RAID management tools and features
– Standards Development: Industry standards for RAID interoperability
Conclusion
Choosing the right RAID configuration is key to managing our data well. There are many options, from simple mirroring to complex nested configurations. RAID technology is great because it lets us balance performance, capacity, and data protection based on our specific needs.
Remember that RAID configuration works hand-in-hand with your NAS operating system choice. While this guide covers the hardware configuration side, your NAS OS provides the software tools and interface for managing these RAID arrays effectively.
When picking a RAID level, we need to look at its features, capacity, and protection level. This helps us decide between performance-focused options like RAID 0 and protection-focused ones like RAID 1 and RAID 5. Each has its own good points and bad, helping us pick the best for our needs.
We should think about how fast, safe, and efficient a RAID configuration is. We also need to consider its performance and features for different use cases. By looking at these things carefully, we can pick a RAID configuration that fits our needs now and in the future.
Ready to implement your RAID strategy? Start by assessing your current storage needs, then choose the configuration that best balances your performance requirements with data protection priorities. Remember, the right RAID setup today can save you from data disasters tomorrow.
FAQ
What is the difference between RAID 1 and RAID 5?
RAID 1 provides complete data mirroring with 50% storage efficiency, while RAID 5 uses distributed parity to protect against one drive failure with better storage efficiency but slower write performance.
How many drives do I need for RAID 5?
RAID 5 requires a minimum of 3 drives. The usable capacity will be the total capacity minus one drive (used for parity data).
Can I change RAID levels without losing data?
Some RAID level changes can be done without data loss, but it depends on your NAS system and the specific change. Always back up your data before attempting any RAID modifications.
What happens if a drive fails in RAID 5?
In RAID 5, if one drive fails, the array continues to operate in degraded mode. You should replace the failed drive as soon as possible to rebuild the array and restore full protection.
Is RAID a substitute for backups?
No, RAID is not a substitute for backups. RAID protects against drive failures, but not against data corruption, accidental deletion, malware, or other data loss scenarios.
Which RAID level is best for home use?
For home use, RAID 1 is excellent for 2-bay systems, while RAID 5 provides a good balance for 4+ bay systems. Consider your data protection needs and storage efficiency requirements.
How long does RAID rebuild take?
RAID rebuild time depends on array size, drive speed, and system performance. Large arrays can take several hours to rebuild. During the rebuild, performance may be reduced.
Can I mix different drive sizes in RAID?
You can mix different drive sizes, but the usable capacity will be limited by the smallest drive. For best performance and reliability, use identical drives.